Asynchronous APIs (Async APIs) are a type of API that allows for communication between two systems without requiring a direct connection between them. This makes them ideal for applications that need to be able to communicate with each other even when they are not online at the same time.
One of the most popular Async API protocols is MQTT. MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol that is well-suited for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. It is also used in a variety of other applications, such as IoT, wearables, and real-time streaming.
Introduction: The Humble Beginnings of MQTT
The year was 1999. Dr. Andy Stanford-Clark from IBM and Arlen Nipper from Arcom (now Eurotech) were grappling with a conundrum: how to provide satellite link communications for oil pipelines? With bandwidth being both scarce and expensive, they needed a protocol that was lightweight and efficient. Enter MQTT – the Message Queuing Telemetry Transport.
“With MQTT, we bridged the gap between communication constraints and the need for real-time monitoring.” – Dr. Andy Stanford-Clark.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to Async API protocols, with a focus on MQTT. We will cover the following topics:
Table of Contents
What are Async APIs?
Async APIs are a type of API that allows for communication between two systems without requiring a direct connection between them. This is done by using a message broker, which is a server that acts as an intermediary between the two systems.
When a system wants to send a message to another system, it does not need to be online at the same time. Instead, it can send the message to the message broker, which will then store the message until the other system is online. When the other system comes online, it can then retrieve the message from the message broker.
Async APIs are ideal for applications that need to be able to communicate with each other even when they are not online at the same time. This is because they do not require a direct connection between the two systems, which can be unreliable and expensive.
What is MQTT?
MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol that is well-suited for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. It is also used in a variety of other applications, such as IoT, wearables, and real-time streaming.
MQTT is a publish-subscribe protocol, which means that messages are published to a topic and then subscribed to by interested parties. This makes it ideal for applications where there are many different systems that need to be able to communicate with each other.
MQTT is a very lightweight protocol, which makes it ideal for devices with limited resources. It is also very efficient, which makes it ideal for applications where messages need to be sent over a limited bandwidth.
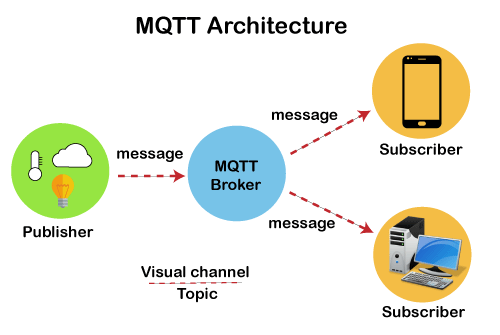
How does MQTT work?
MQTT works by using a client-server architecture. The clients are the systems that want to send or receive messages, and the server is the message broker.
When a client wants to send a message, it first connects to the message broker. The message broker then assigns the client a unique identifier, which is used to identify the client in all subsequent communications.
The client then publishes the message to a topic. The topic is a name that identifies the type of message that is being published. For example, a topic might be sensors/temperature or devices/light.
Any client that is subscribed to the topic will then receive the message. The client can then process the message as needed.
- Publisher/Subscriber Model: Unlike traditional protocols where devices have to request data explicitly, MQTT-enabled devices can subscribe to specific topics and receive updates automatically.
- Broker: At the heart of MQTT lies the broker. It is responsible for receiving all messages, filtering them, and deciding correctly where to distribute them.
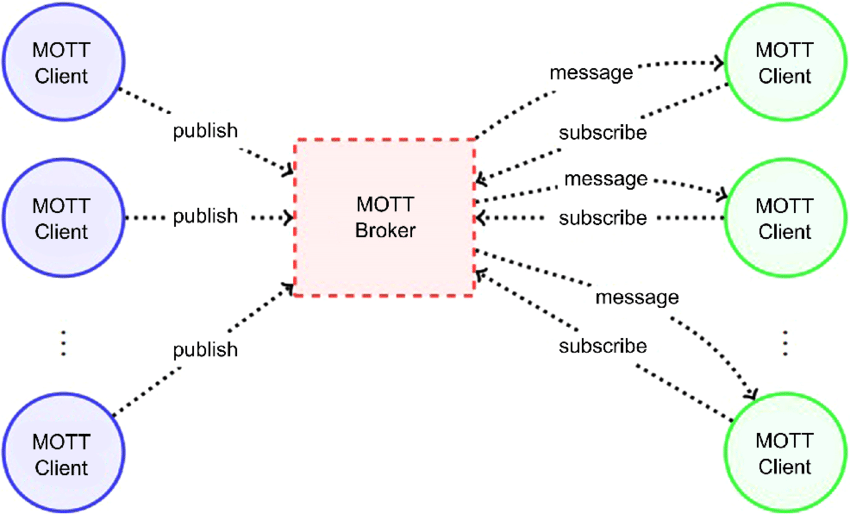
MQTT Unwrapped: Simplicity yet Powerful
At its core, MQTT is a publish/subscribe messaging protocol designed for lightweight data flow with a focus on reliability and bandwidth efficiency.
Features of MQTT:
- Small Size: Designed to support connections with remote locations where the network might be expensive or unreliable.
- Real-time: Ensures the rapid relay of information, which is essential in scenarios like emergency alerts.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Offers three levels to maintain the balance between speed and reliability.
The benefits of using MQTT
There are many benefits to using MQTT, including:
- Lightweight and efficient: MQTT is a very lightweight protocol, which makes it ideal for devices with limited resources. It is also very efficient, which makes it ideal for applications where messages need to be sent over a limited bandwidth.
- Scalable: MQTT is a scalable protocol that can be used to support a large number of clients and topics.
- Reliable: MQTT provides a number of features that ensure the reliable delivery of messages, such as QoS (quality of service).
- Secure: MQTT can be used to secure messages using a variety of encryption methods.
- Open source: MQTT is an open source protocol, which means that it is free to use and develop.
Use cases for MQTT
MQTT is used in a variety of applications, including:
- IoT: MQTT is a popular choice for IoT applications because it is lightweight and efficient. It is also well-suited for applications where there are many different devices that need to be able to communicate with each other. For example, MQTT can be used to send sensor data from devices to a central server, or to control devices remotely.
- Wearables: MQTT is also used in wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers. This is because it is a low-power protocol that can be used to send data from the wearables to a mobile device or server.
- Real-time streaming: MQTT can also be used for real-time streaming applications, such as live video streaming or stock market data. This is because MQTT provides a reliable way to send messages in real time.
- Enterprise applications: MQTT is also used in enterprise applications, such as supply chain management and logistics. This is because MQTT can be used to connect different systems and applications together, and to automate workflows.
How to implement MQTT
There are many different ways to implement MQTT. One way is to use a commercial MQTT broker, such as HiveMQ or Mosquitto. These brokers provide a turnkey solution that makes it easy to get started with MQTT.
Another way to implement MQTT is to use an open source MQTT broker, such as Eclipse Mosquitto. These brokers are free to use and can be customized to meet specific needs.
Once you have chosen an MQTT broker, you can then start using MQTT to connect your systems and applications together.
The future of Async API protocols
Async API protocols are becoming increasingly popular as the need for reliable and efficient communication between systems grows. MQTT is one of the most popular Async API protocols, and it is likely to continue to be used in a wide variety of applications in the future.
Here are some of the trends that are driving the growth of Async API protocols:
- The rise of the IoT: The IoT is creating a need for new ways to connect devices and applications together. Async API protocols are well-suited for this, as they can be used to connect devices with limited resources.
- The growth of cloud computing: Cloud computing is making it easier to deploy and manage Async API protocols. This is making them more accessible to a wider range of users.
- The increasing demand for security: Async API protocols are becoming more secure, as they are being used in more critical applications.
Overall, the future of Async API protocols looks bright. They are well-suited for a wide range of applications, and they are becoming increasingly popular as the need for reliable and efficient communication grows.
